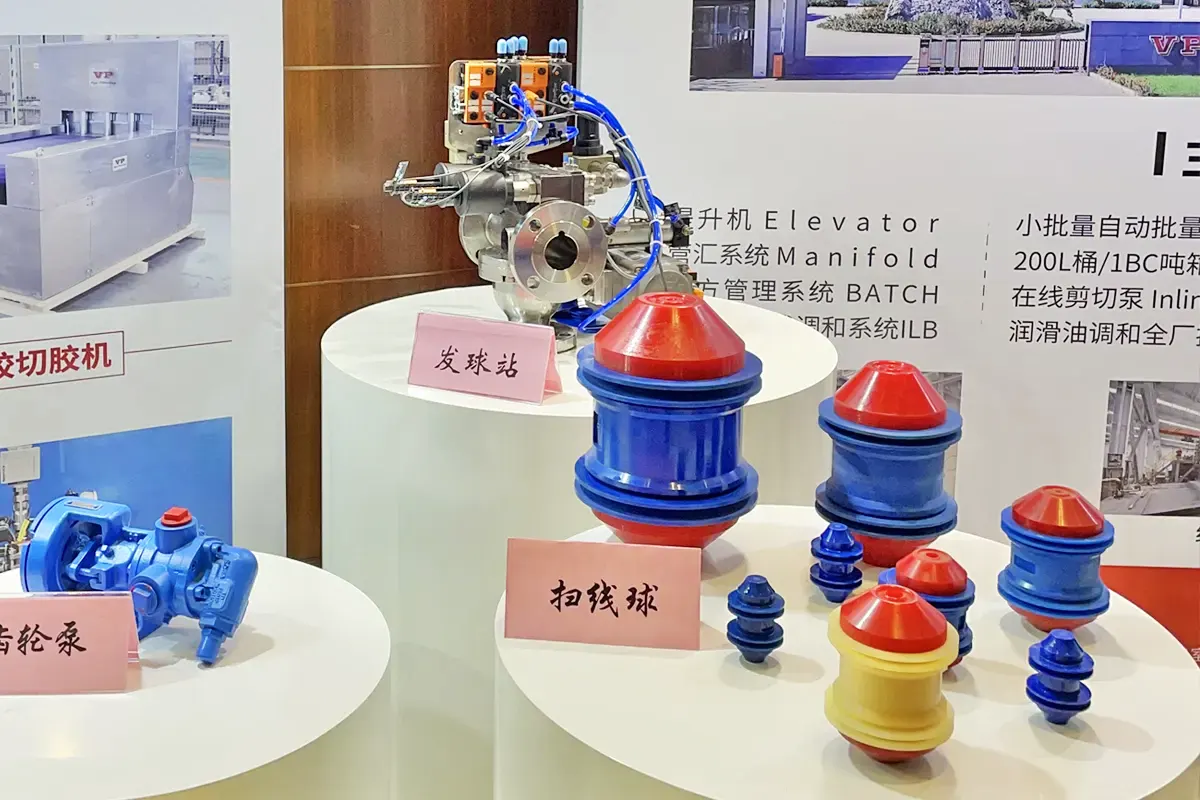
A pigging system efficiently recovers product residue and cleans pipelines through the coordinated operation of its core components. Below are the essential parts and their functions:
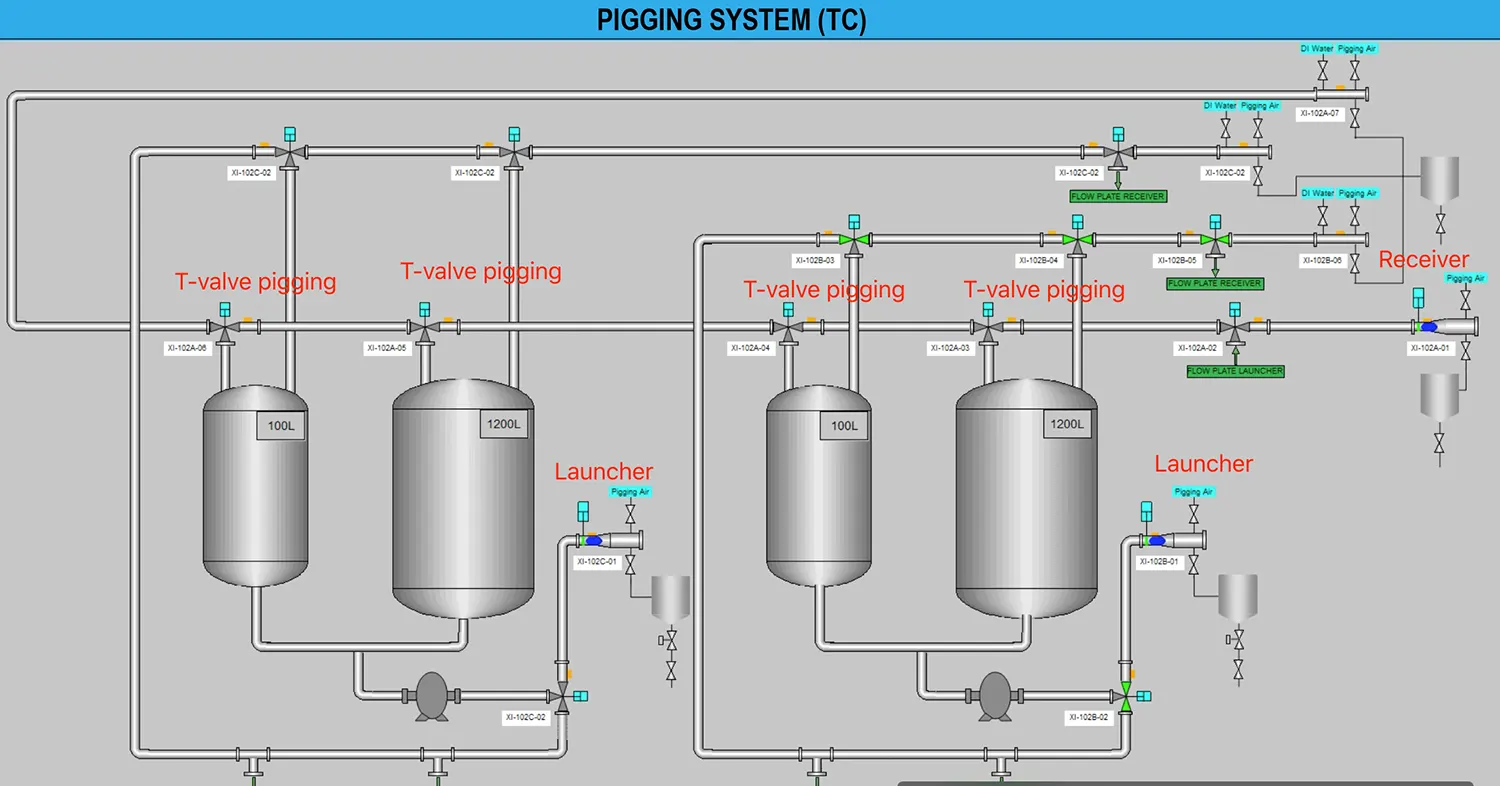
1. Pig (Pigging Ball)
Function: The primary actuator that physically contacts the pipe wall to push out residual product, remove deposits, or separate media.
Types:
- Solid Spheres (Silicone/Polyurethane): Hygienic-grade, easy to clean.
- Multi-component Pigs (with scrapers/brushes): For viscous/solid residues in industrial applications.
- Smart Pigs (with sensors): Detect pipe deformations, corrosion, or temperature (advanced use).

Material Selection:
- Hygienic: FDA-grade silicone/polyurethane, high-polish, non-toxic.
- Industrial: Wear-resistant polyurethane, acid-proof rubber, or composites for high-pressure/corrosive environments.
2. Launcher Station
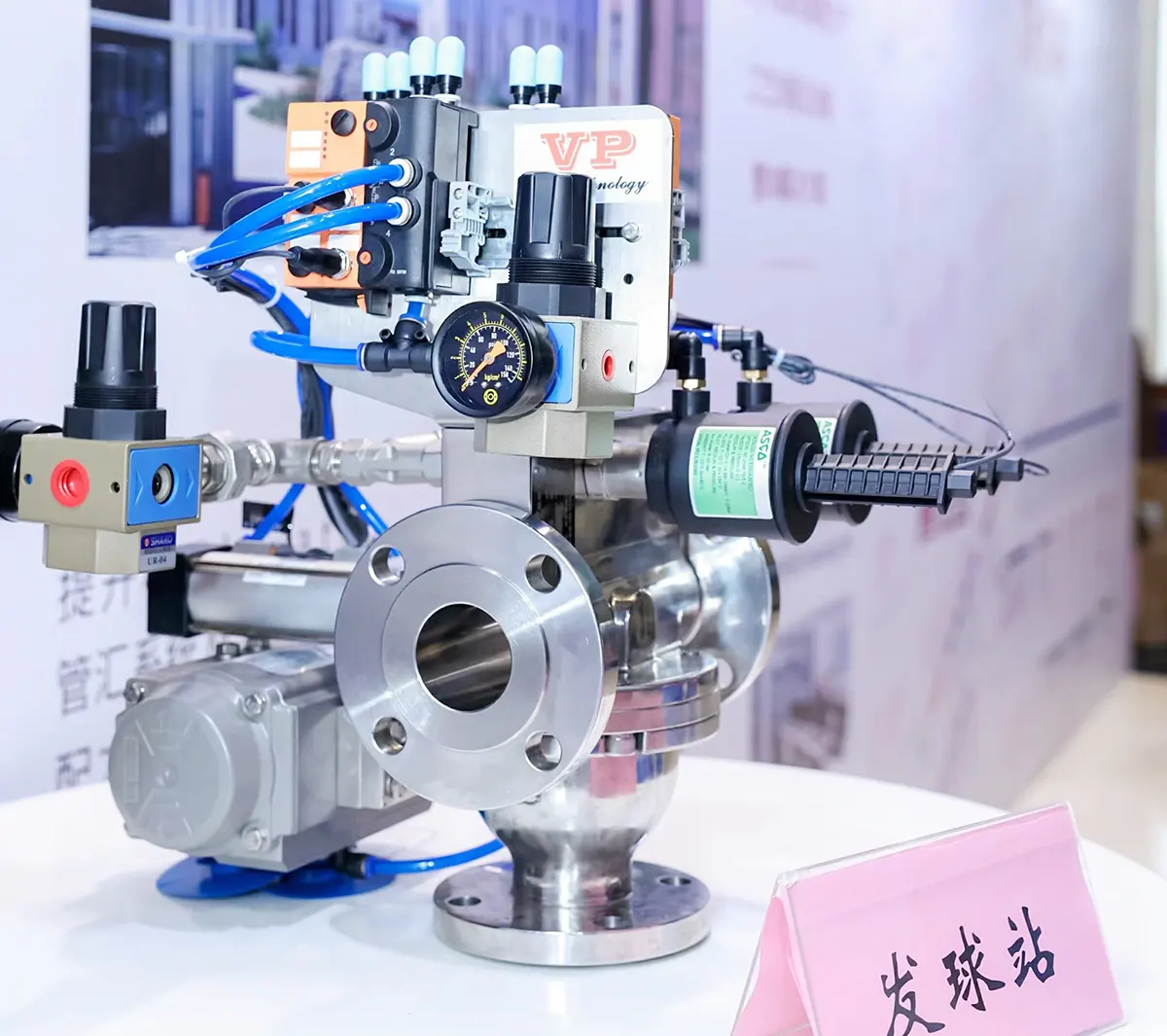

Function: The entry point for deploying pigs, typically at the pipeline start.
- Pressure vessel (barrel)
- Quick-opening closure (Tri-Clamp for hygienic, flanged for industrial)
- Medium injection valve (gas/liquid to propel the pig)
- Pressure/position sensors
Example Models: VP ASHLDV (hygienic), standard industrial launchers.
3. Receiver Station
 Function: Captures and retrieves pigs at the pipeline end.
Function: Captures and retrieves pigs at the pipeline end.
Design Features:
- Buffer mechanism (reduces pig impact)
- Discharge valve (removes residual media/product)
- Sight glass (hygienic-grade for easy inspection)
Example Models: VP ASRLDV (hygienic), industrial receivers.
4. Control System
In a pigging system, the equipment requires a control system (which can also operate manually). Using real-time pressure sensor data, it precisely regulates valve opening/closing and controls the pig’s movement inside the pipeline.
Typically, to integrate with other systems (ABB, SMB, manifold), the pigging system can operate in coordination with them and be centrally monitored by a Distributed Control System (DCS). This ensures automated, safe, and efficient pigging operations.
For example, in an SMB system:
- When the flow meter reaches the preset value, it signals the valve to close.
- After valve closure, it notifies the ball launcher to begin purging.
- The launcher then requests the downstream destination to open its valve.
- Once downstream confirms the valve is open, the launcher immediately initiates the purge operation.
5. Medium Propulsion Device
Function: Provides driving force (gas/liquid) to move pigs.
Key Components:
- Compressed gas/liquid source (N₂, air, water, or process fluid)
- Filter regulator valve (regulate flow/pressure for smooth operation)
- Pressure gauges & sensors (real-time monitoring)
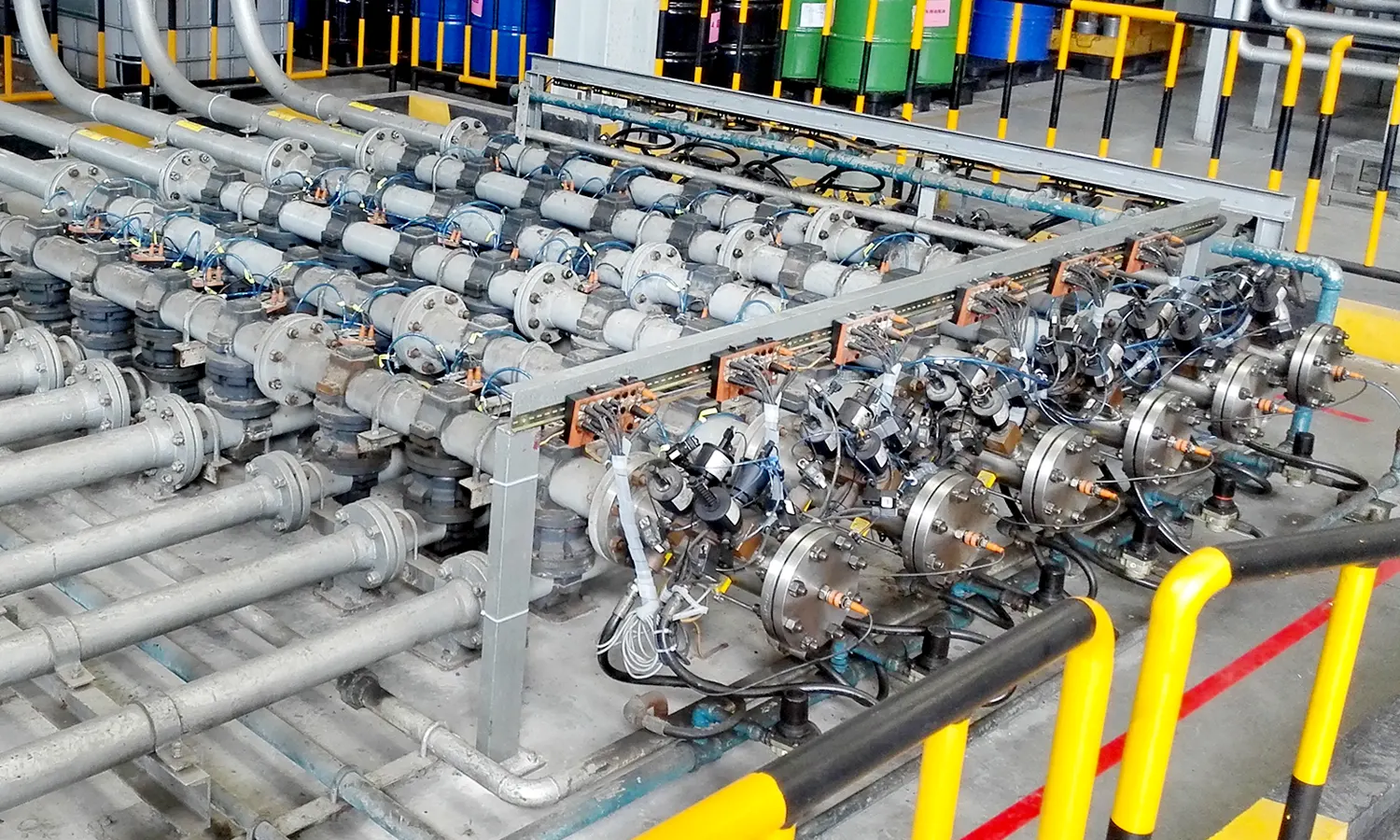
6. Pipeline Connections & Valves
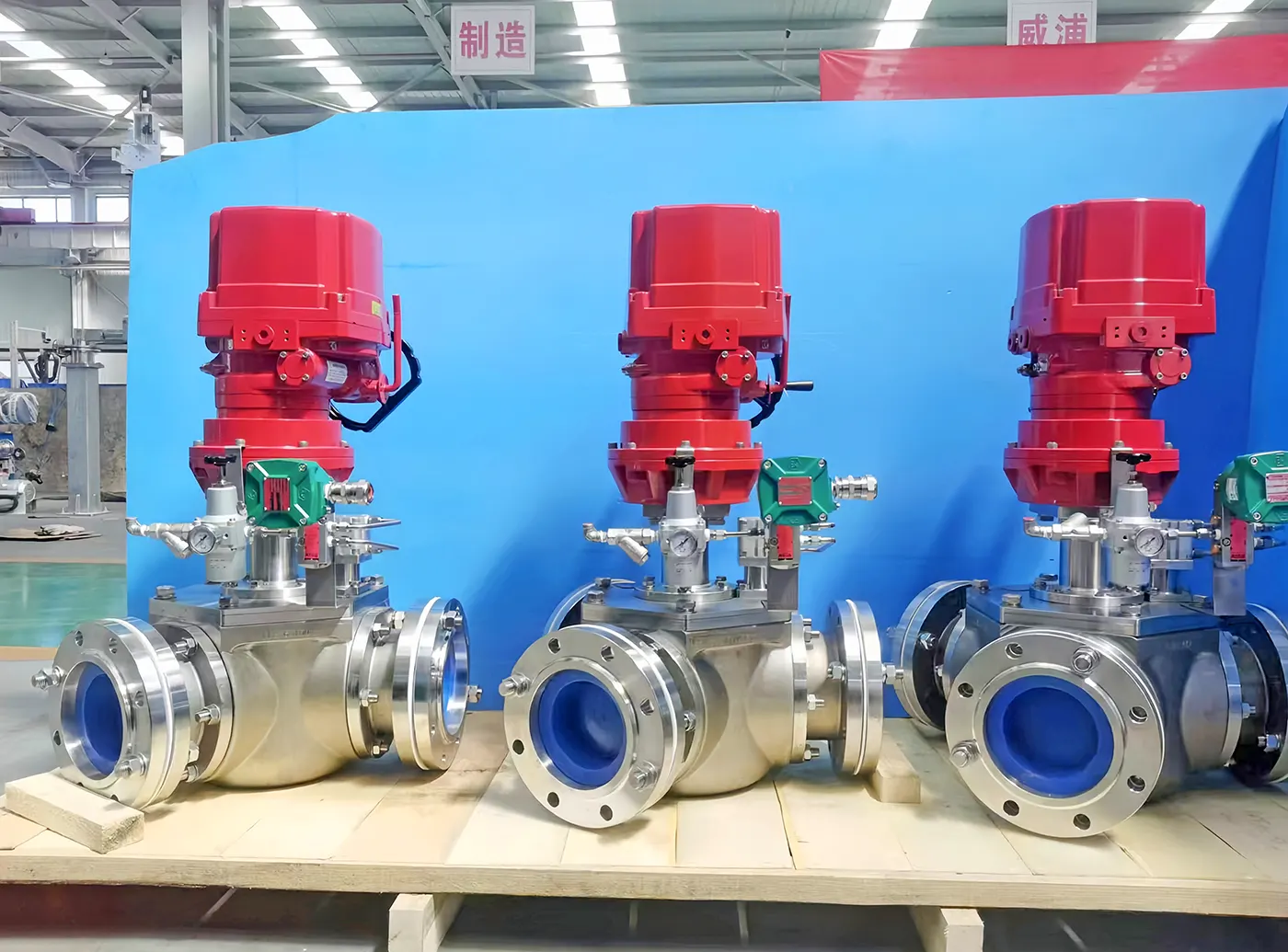

Hygienic-Grade:
- Tri-Clamp fittings: Quick disassembly, dead-space-free, 3-A/SMS compliant.
- Sanitary valves (butterfly/ball): Polished internals, CIP/SIP compatible.
Industrial-Grade:
- Welded/flanged connections: High-pressure (>Class 600) and high-temperature (>200°C) resistant.
- Pigable valves: Guide pigs to avoid branch pipelines.
7. Auxiliary Equipment
- Pig Loader/Unloader: Safely installs/removes pigs without contamination (hygienic) or high-pressure risks (industrial).
- Intermediate Station (e.g., ASILDV): Enables pigging in long/complex pipelines.
- 3-Way Diverter (e.g., 3W): Routes pigs in multi-branch pipelines.
System Integration Key Parameters
| Component | Hygienic-Grade Specs | Industrial-Grade Specs |
|---|---|---|
| Pipe Size | 1.5″ – 8″ (high precision) | 2″ – 48″+ (standard) |
| Connection Type | Tri-Clamp | Welded/ANSI Flange |
| Valve Type | Sanitary Butterfly + CIP Port | Pig Valve + High-Pressure Gate |
| Pig Material | FDA Silicone/Polished | Abrasion-Resistant PU/NBR |
| Pressure Rating | Up to 10 bar | Up to 400 bar |
Why Are These Components Indispensable?
- Pig: Directly affects cleaning/recovery efficiency.
- Launch/Receive Stations: Ensure safe pig entry/exit.
- Control System: Manages the pig’s movement within the pipeline and integrates with other systems (ABB, SMB, manifold) to enable full-process automation.
- Propulsion System: Provides consistent driving force.
- Valves & Piping: Maintain system integrity (leak-proof in industrial, contamination-free in hygienic).
- Auxiliary Stations: Enable complex pipeline configurations (long-distance, multi-branch).

Example Scenario: In a dairy plant (hygienic grade), a pig is launched from the ASHLDV station, propelled by nitrogen through Tri-Clamp piping, recovering 99.6% of high-value yogurt, and finally captured at the ASRLDV station, triggering automatic CIP cleaning. In a chemical plant (industrial grade), a split pig starts from a flanged launching barrel, clearing viscous resin residues, withstands 50 bar pressure and 80°C high temperature, and is guided to the receiving barrel via a kicker valve.
Understanding these core components and their synergy is critical for optimizing pigging system design, maximizing recovery rates, and reducing operational costs.
Articles Related
-

Piggable Ball Valve: Full Bore Isolation Valve Designed for Pigging
The Piggable Valve (Full Bore Ball Valve for Pigging) is specifically designed for pipeline pigging s...
-

VP Pigging System: Efficiency Pipeline Cleaning & Recovery
The pigging system (also known as ball-pigging system or product recovery system) is specialized equi...
-

Piggable Tee: Key Fitting for Efficient Pigging
The Piggable Tee is a specialized pipeline component designed for Pipeline Pigging systems. Its prima...




