Pigging systems launch “pigs” (cleaning devices) through pipelines, using media (compressed gas/liquid) to efficiently remove and recover residual materials, achieving pipeline cleaning and product recovery. Based on core application requirements, they are primarily categorized into Hygienic Pigging Systems and Industrial Pigging Systems, with significant differences in objectives, applications, design standards, and key components.
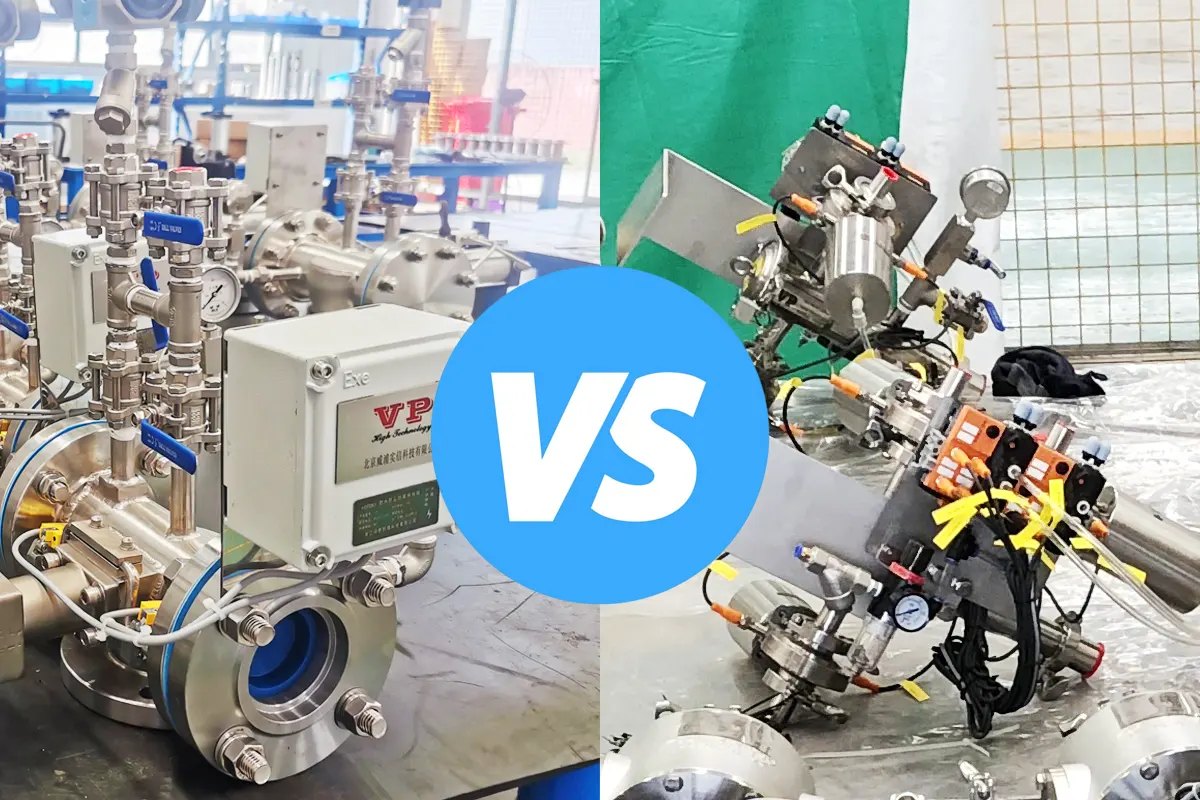
Core Differences Overview
1. Primary Objectives:
- Hygienic: Primary focus is ultimate cleanliness, zero residue, and contamination prevention. Ensures product-contact surfaces meet stringent sanitary standards, prevents cross-contamination. Product recovery is important but must not compromise cleanliness or safety.
- Industrial: Core goals are efficient product recovery, residue removal, and pipeline optimization while withstanding extreme conditions (high temperature/pressure, corrosive media, frequent operation). Emphasizes cost-effectiveness (maximizing recovery rate, reducing waste) and process reliability.
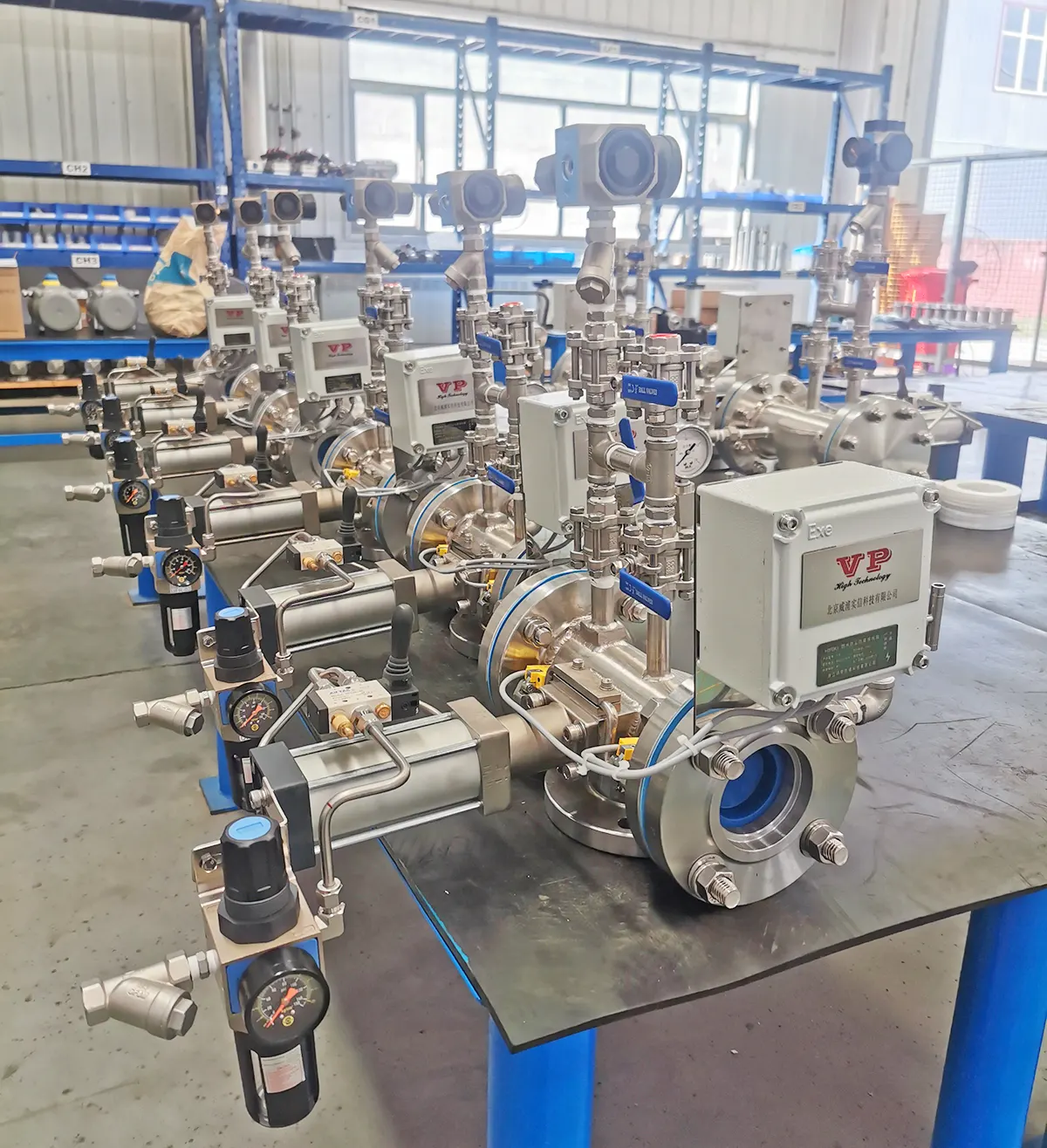

2. Key Industries:
- Hygienic: Food & beverage, dairy, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, cosmetics – industries requiring highest hygiene standards.
- Industrial: Oil & gas, petrochemicals, chemicals, paints, lubricants – industries handling hazardous, viscous, or high-value media in demanding
pipeline environments.
3. Design & Material Standards:
Hygienic:
- Materials: All product-contact surfaces (pipe interiors, pigs, valve seals, launcher/receiver chambers) are typically constructed from 304SS or 316SS (sometimes 316L). They feature extremely low surface roughness (typically Ra ≤ 0.8 μm) and undergo polishing (mechanical or electropolishing), ensuring: Dead-space-free design, Effortless cleaning, Superior corrosion resistance, Prevention of bacterial growth.
- Connections: Widely use sanitary quick-connect clamps (e.g., Tri-Clamp) for rapid disassembly, thorough cleaning, and inspection.
- Cleaning Protocols: Mandatory post-pigging CIP (Clean-in-Place) or SIP (Sterilize-in-Place) using water, detergents, or steam to ensure sterile, residue-free systems.
Industrial:
- Materials: Prioritize pressure, temperature, wear, and chemical corrosion resistance. Common materials include carbon steel, alloy steel, or engineered plastics. Surface finish requirements are lower than hygienic systems, with greater focus on structural strength and durability.
- Connections: Primarily use welded or flanged joints for superior sealing and high-pressure/temperature tolerance, suitable for long-distance transfer or demanding processes.
- Durability: Designed to withstand frequent operation, high pressure/temperature, and corrosive/abrasive media.
4.System Components & Parameters:
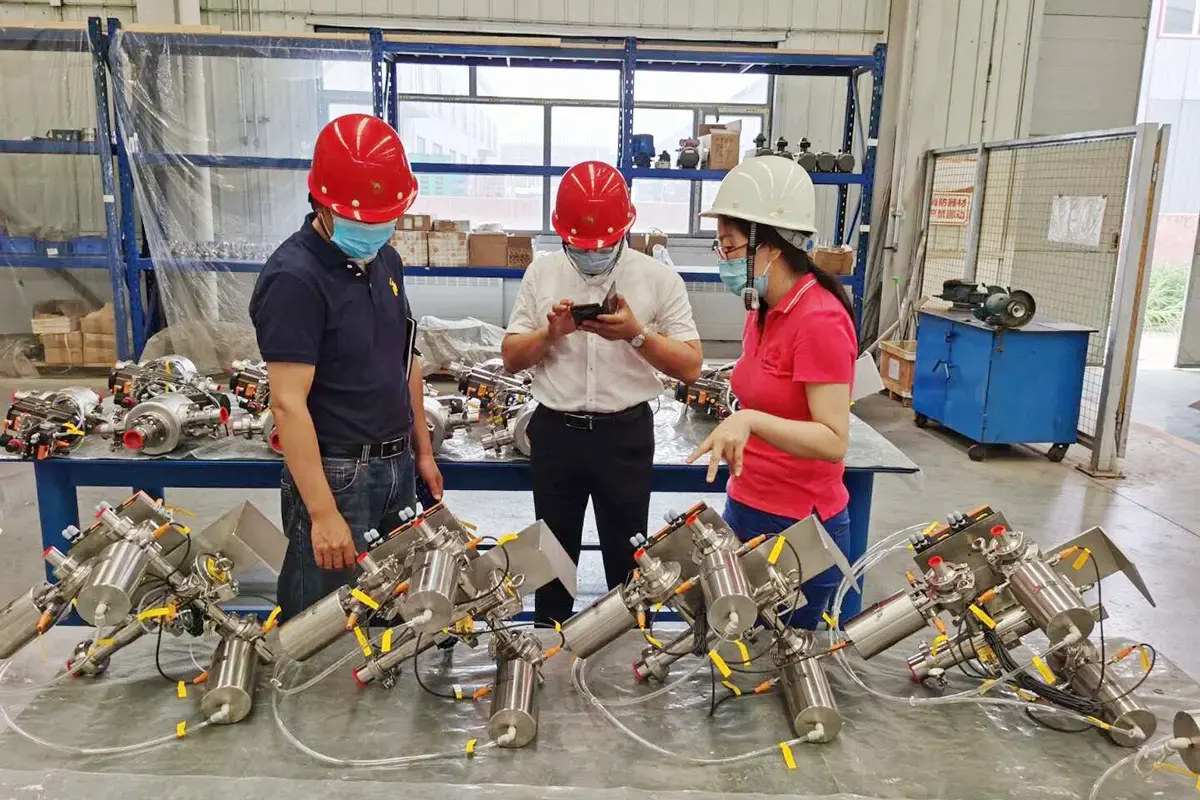
- Shared Components: Both include launch stations (pipeline start), receive stations (pipeline end), control valves (media regulation), pigs (core components), and pig retrievers for maintenance. The WAP pigging principle (liquid displacement via pigs) applies to both.
- Component Differentiation: Hygienic system components (stations, valves, pipes) must comply with sanitary design standards for materials, surface finish, and connections. Industrial components emphasize structural strength and sealing.
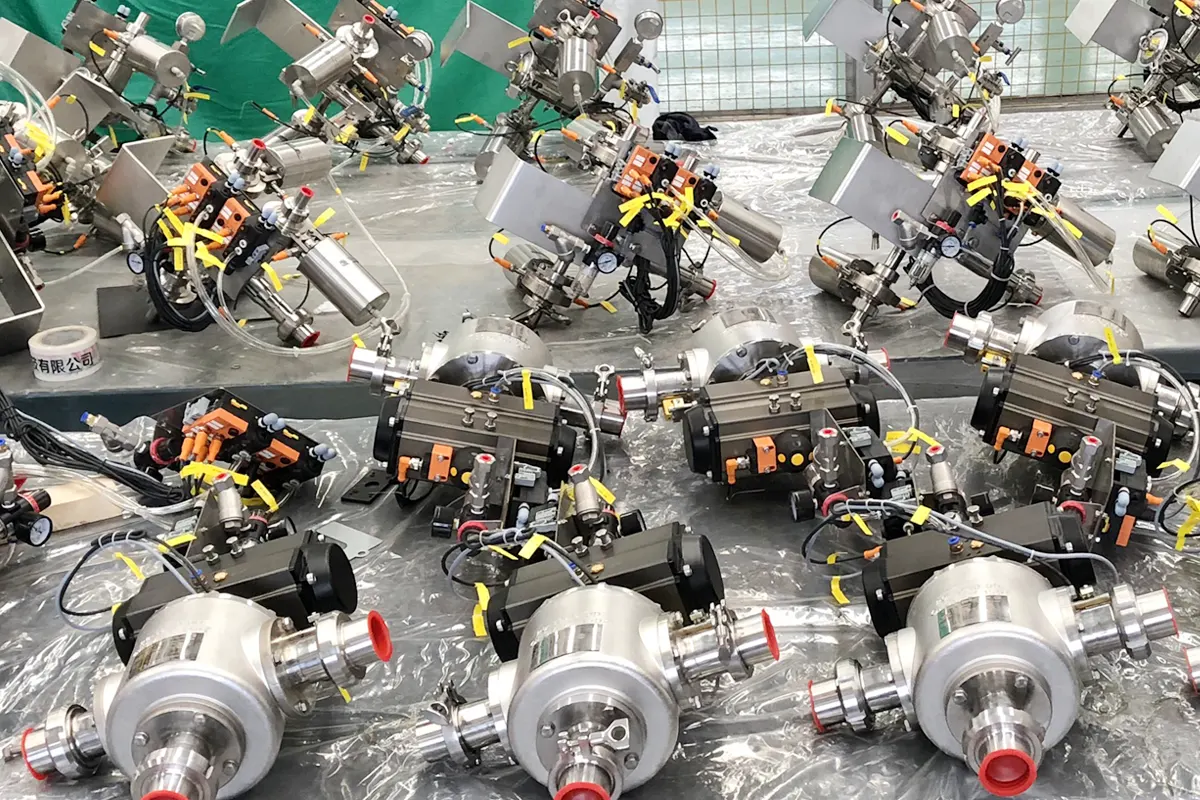

Typical Parameter Ranges:
- High-Precision Systems (Hygienic/High-demand industrial): Smaller diameters (1.5″ – 8″). Include precision launch/receive stations (e.g., ASHLDV/ASRLDV), intermediate stations (ASILDV), 3-way diverters (3W), and (separable) pigs with retrievers.
- Standard Pipeline Systems (Industrial): Larger diameters (8″ and above). Feature heavy-duty pig launchers/receivers, piggable tees, ball valves, and pigs focused on robustness.
Core Comparison: Hygienic vs. Industrial Pigging Systems
| Feature | Hygienic Pigging Systems | Industrial Pigging Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Core Objective | Ultimate cleanliness, zero residue, contamination-free | Efficient recovery, residue removal, withstand harsh conditions |
| Key Industries | Food & beverage, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, cosmetics | Oil & gas, petrochemicals, chemicals, paints, lubricants |
| Critical Requirements | Fully Automated Pipeline Draining and Efficient Cleaning (Replacing Manual Operations) | Maximize recovery rate (>99%), withstand high pressure/temperature/corrosion, high reliability |
| Material Standards | Product-contact surfaces: Highly polished 316L stainless steel (Ra≤0.8μm), no dead zones | Carbon steel, alloy steel, engineered plastics; focus on pressure/wear/corrosion resistance |
| Connection Method | Sanitary quick-connect clamps (Tri-Clamp) for rapid disassembly/cleaning | Welded or flanged connections, high sealing, withstand high pressure/temperature |
| Cleaning Requirements | Mandatory CIP/SIP post-pigging (water/detergents/steam) | Typically no complex cleaning; relies on pig effectiveness |
| Resistance | Meet sanitary standards, moderate temperature/pressure tolerance | Must withstand high pressure/temperature, corrosive media, frequent operation |
| Typical Diameter | Commonly smaller diameters (e.g., 1.5″ – 8″) | Wide range, especially large diameters (e.g., 8″+) |
| System Component Examples | Precision launch/receive stations (ASHLDV/ASRLDV), intermediate stations (ASILDV), 3-way diverters(3W) | Standard pig launchers/receivers, piggable tees, ball valves, pigs |
| Pig Materials | Sanitary-compliant (e.g., food-grade silicone, polyurethane), smooth surface | Diverse materials, focus on wear/chemical resistance, sealing |

Selection Guide
Choosing between hygienic and industrial pigging systems depends fundamentally on specific industry requirements:
- For processes involving human consumption, pharmaceutical safety, or strict hygiene standards, hygienic systems are mandatory. Their design and materials eliminate contamination risks.
- For applications prioritizing efficient recovery of high-value/hazardous products, extreme conditions (high pressure/temperature/corrosion), or long-distance pipelines, industrial systems offer optimal solutions through robustness, tolerance, and cost-effectiveness.
Understanding these core differences enables selection of the most suitable, efficient, and compliant pigging solution for specific applications.
Articles Related
-
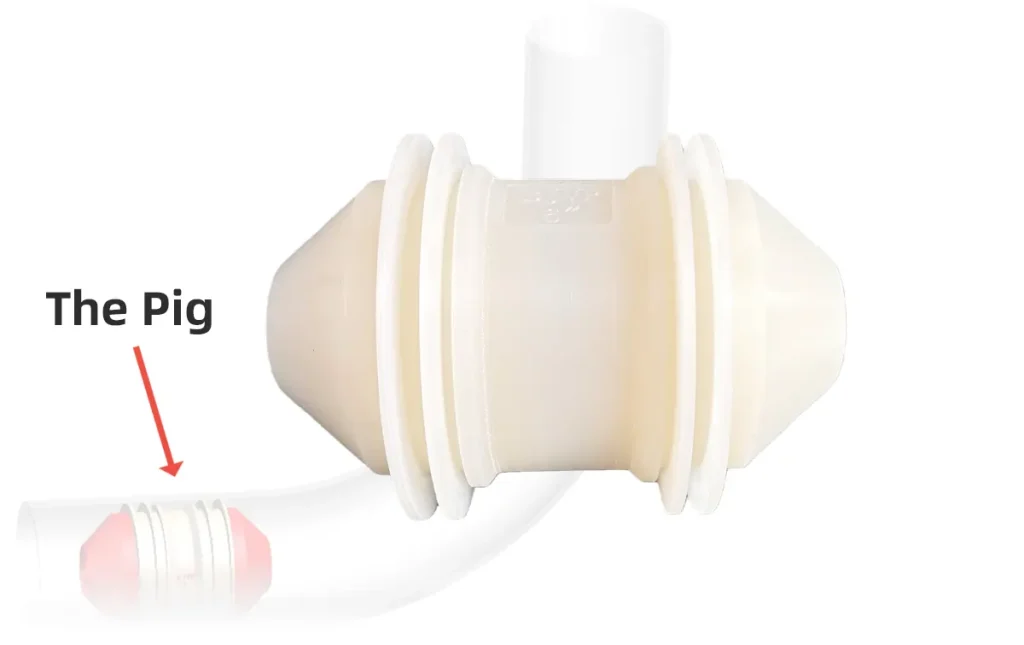

High-Temperature Polyurethane Pipeline Cleaning Pig
BJVP High-Temperature Polyurethane Pipeline Cleaning Pig is an elastic device slightly larger than th...
-

VP’s Synthetic Grease QA Framework Wins Acclaim at 2025 Symposium
June 23-24, 2025 – The highly anticipated “Synthetic Oil & Greases Technology and Marketin...
-

2025 China International Coatings Exhibition, Invitation from BJVP(Nov 25–27)
Dear Customers and Partners, Greetings! We sincerely invite you to visit the 2025 China International...




